Revolutionizing MMW Systems: The Crucial Role of Cryogenic Isolators
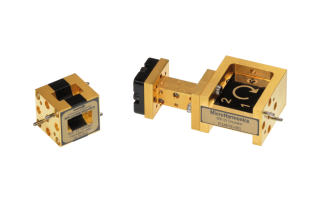
Revolutionizing MMW Systems: The Crucial Role of Cryogenic Isolators Millimeter wave engineers operate in a part of the electromagnetic spectrum where there are some significant challenges to overcome. It is difficult to generate signal power, the available components are costly and sometimes don’t work well, and often the components just don’t exist at these frequencies. In fields such as radio astronomy, designers must go to [...]
Two Methods for Realizing Millimeter Wave Isolators
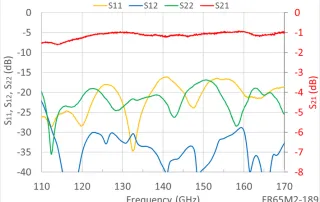
Two Methods for Realizing Millimeter Wave Isolators There are two fundamentally different techniques for designing isolators at millimeter-wave (MMW) frequencies. Maybe you have noticed this if you ever wondered why some isolators are narrow-band and some operate across the full waveguide band. Or maybe you noticed that some isolators are built with a terminated third port and some only have two ports. These differences (and [...]
Some Interesting Facts About Rectangular Waveguides
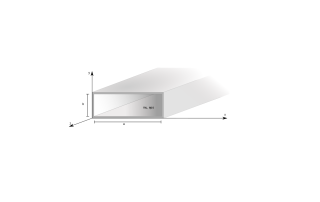
Some Interesting Facts about Rectangular Waveguides David W. Porterfield, Ph.D., Micro Harmonics Corporation Rectangular waveguides are commonly used in mm-wave applications primarily because they are the lowest loss transmission media at these frequencies. They are single-moded over broad bandwidths and provide isolation from external RF signals. In this post, we will review some other interesting facts about rectangular waveguides and hopefully provide some helpful tips. [...]
The Difficulties in Writing Specifications for Millimeter-Wave Components
The Difficulties in Writing Specifications for Millimeter-Wave Components Introduction We often accept a manufacturer’s specification of their millimeter wave components without a second thought. But a survey of the industry will reveal that what one manufacturer means by, for example, “20 dB isolation” could be a very different standard of performance from another manufacturer who makes the same claim. This is partially because of inherent difficulties [...]
How to Choose an Isolator for a Millimeter-Wave System
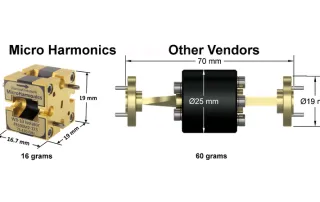
How to Choose an Isolator for a Millimeter-Wave System Millimeter-wave (MMW) systems often employ isolators to suppress standing waves and achieve optimal performance. Isolators pass an RF signal traveling in the forward direction while absorbing signals traveling in the reverse direction. The absorbed signal is converted to heat energy in a resistive load internal to the isolator. There are a number of ways to implement [...]
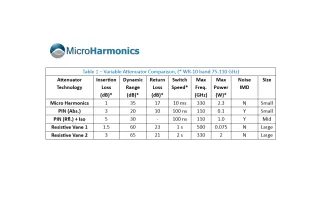
A Comparison of Millimeter-Wave Variable Attenuator Technologies
A Comparison of Millimeter-Wave Variable Attenuator Technologies Electronically tunable variable attenuators are useful for signal leveling and switching applications. The desirable characteristics of an attenuator are typically high power handling, high dynamic range, high return loss (low port reflections), a high degree of flatness in the response across the band, low insertion loss, and broad bandwidth. Size, weight, switching speed, and intermodulation distortion (IMD) can [...]