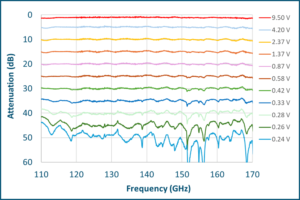
Our attenuators use Faraday rotation in a ferrite rod to rotate an RF signal into a fixed resistive vane. The attenuation level is set using a simple DC voltage in the range from 0 – 9.5 V. They are configured so that maximum attenuation is achieved at 0 V bias. Models are currently available at WR-10, WR-8, and WR-6.5 with additional models planned for every band from WR-15 through WR-3.4. Measured data from our D-band WR-6.5 attenuator is shown below. The dynamic range is more than 35 dB. The WR-6.5 attenuator has a power rating of 1.5 W. Our attenuator has a flatter response, higher return loss, higher power handling, higher dynamic range, and higher frequency coverage than a PIN attenuator.
 |
| WR-6.5 attenuator |
Our WR-6.5 attenuator is shown to the left. The attenuator is lightweight and compact with the main body measuring (0.75 x 0.75 x 1.2 inch) (19 x 19 x 30 mm). The small size makes the attenuator very easy to fit into millimeter-wave systems. A DC control voltage is applied through an SMP (M) connector.
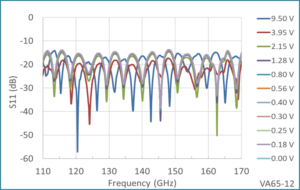
An important advantage of the ferrite attenuator is the relatively low port reflections. The graph below shows measured reflections on Port 1 at the various attenuation levels of the WR-6.5 attenuator. The reflections are less than -14 dB across the band for every attenuation level. This compares favorably to the port reflections found on PIN attenuators which can approach -5 dB.
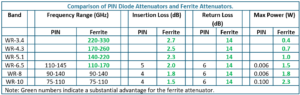
Our ferrite attenuator is compact, lightweight, and has no moving parts. The technology is passive and insensitive to ESD damage. CVD diamond discs are used to channel heat away from the ferrite rods and resistive vanes which enables our ferrite attenuators to handle significantly higher power levels than PIN attenuators. The table below shows a comparison of insertion loss, return loss (port reflections), and maximum power for both our ferrite attenuators and the PIN attenuators offered by other vendors. The comparison is shown for the mm-wave bands from WR-10 through WR-3.4.